Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
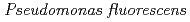 in the presence of organic ligands
in the presence of organic ligandsYoshida, Takahiro; Suzuki, Yoshinori*; Ozaki, Takuo; Onuki, Toshihiko; Francis, A. J.*
Proceedings of International Symposium on Radioecology and Environmental Dosimetry, p.296 - 300, 2004/03
The effects of organic ligands (citric acid, desferrioxamine B (DFO) and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA)) on Eu(III) adsorption by an aerobic bacterium 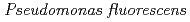 were investigated. After incubation of
were investigated. After incubation of  with 2
with 2  M Eu(III) without organic ligands in a 0.1 M NaCl solution containing 3.9 mg
M Eu(III) without organic ligands in a 0.1 M NaCl solution containing 3.9 mg /L biomass for 1 hour, over 90% Eu(III) was adsorbed on the bacterial cells at pH 4 - 7. Eu(III) adsorption by bacterial cells was depleted at pH 4 - 7 when equimolar EDTA was present, while citric acid and DFO showed less effect on the depletion of Eu(III) adsorption. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) indicated that the adsorbed Eu(III) on cells was covalently bound to carboxyl and/or hydroxyl functional groups of the cell surface. These results suggest that carboxyl and/or hydroxyl functional groups of cell surface show a higher affinity with Eu(III) than citric acid and DFO and have the potential to prevent migration of Eu-organic ligands complexes with low stability constants in environments.
/L biomass for 1 hour, over 90% Eu(III) was adsorbed on the bacterial cells at pH 4 - 7. Eu(III) adsorption by bacterial cells was depleted at pH 4 - 7 when equimolar EDTA was present, while citric acid and DFO showed less effect on the depletion of Eu(III) adsorption. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) indicated that the adsorbed Eu(III) on cells was covalently bound to carboxyl and/or hydroxyl functional groups of the cell surface. These results suggest that carboxyl and/or hydroxyl functional groups of cell surface show a higher affinity with Eu(III) than citric acid and DFO and have the potential to prevent migration of Eu-organic ligands complexes with low stability constants in environments.